When choosing membrane pore size for vacuum filtration, consider your sample’s particle size and filtration goals. Larger pores allow faster filtration and reduce clogging but may let smaller particles pass through, affecting purity. Finer pores improve separation but slow the process and can cause fouling if mismatched with your sample. Maintaining proper pore size guarantees efficient filtration and membrane longevity. Keep exploring to discover how to fine-tune your setup for ideal results.
Key Takeaways
- Match membrane pore size to the particle size of your sample to optimize separation and reduce fouling.
- Larger pores allow faster filtration but may permit unwanted particles; smaller pores improve purity but slow down the process.
- Consider sample properties and filtration goals—prioritize speed or purity when choosing pore size.
- Regularly inspect membranes for fouling or damage to maintain consistent filtration efficiency.
- Select membrane materials compatible with your solvents and samples to prevent degradation and ensure longevity.
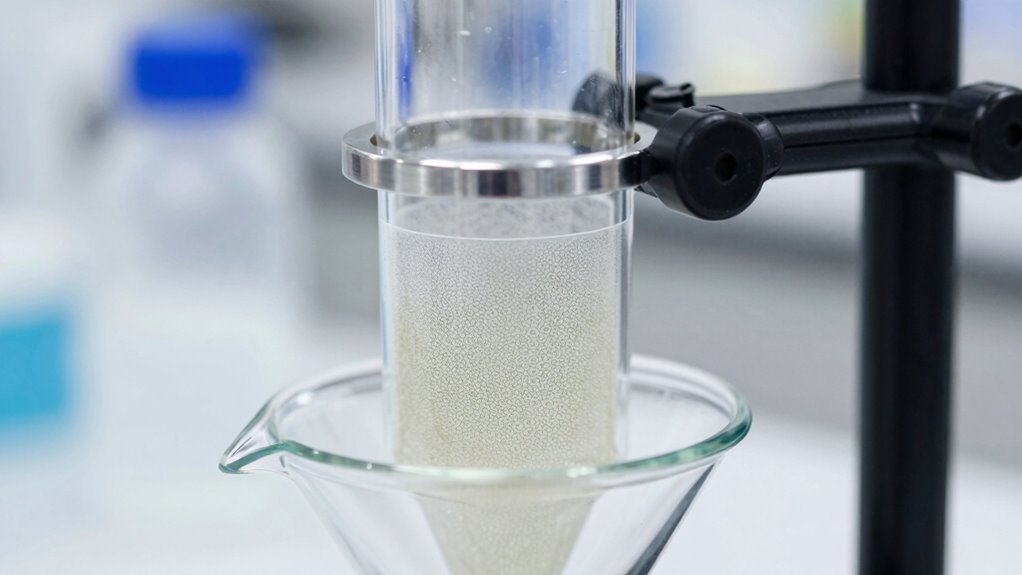

Vacuum filtration is a common laboratory technique used to quickly and efficiently separate solids from liquids. When you’re performing vacuum filtration, one of the key factors influencing your results is selecting the right membrane pore size. The pore size determines which particles are retained and which pass through, directly impacting the filtration efficiency. If your membrane’s pores are too large, smaller particles may slip through, leading to incomplete separation. Conversely, choosing a membrane with pores that are too small can slow down filtration and increase the risk of membrane fouling, which can reduce your process’s overall effectiveness.
Membrane fouling is a significant challenge in vacuum filtration, especially when working with complex or highly concentrated samples. Fouling occurs when particles, microorganisms, or other materials clog the pores or surface of the membrane, diminishing its permeability. This clogging not only hampers filtration speed but also compromises filtration efficiency, as it becomes harder for liquids to pass through freely. To minimize fouling, you should carefully consider the pore size relative to your sample’s particle size, aiming for a balance that maximizes throughput without sacrificing separation quality. Pre-filtering or diluting samples can also help prevent rapid fouling and extend the lifespan of your membrane.
Filtration efficiency hinges on selecting a membrane that matches your sample’s characteristics and your experimental goals. If you’re filtering a mixture with a broad particle size distribution, opting for a membrane with a slightly larger pore size can prevent clogging while still capturing the majority of solids. On the other hand, if you need a highly purified filtrate, choosing a finer pore size will improve your results but may require longer filtration times and more frequent membrane maintenance. Regularly monitoring filtration progress and inspecting your membrane for signs of fouling will help you make adjustments as needed, ensuring consistent performance. Understanding membrane material properties can also influence your choice and help prevent unintended fouling or degradation.
Another consideration is the material of your membrane, as different materials offer varying resistance to chemicals and temperature, which can influence fouling tendencies and filtration efficiency. Selecting a membrane compatible with your sample and solvent system helps prevent unwanted interactions that could lead to fouling or membrane degradation. Proper handling, cleaning, and maintenance also play vital roles in sustaining membrane performance over multiple uses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Membrane Pore Size Affect Filtration Speed?
Yes, membrane pore size can affect filtration speed. When you optimize pore size, you improve filtration efficiency, but smaller pores slow down flow rates because they create more resistance. Conversely, larger pores allow faster filtration but might compromise the filtration’s effectiveness. By focusing on pore size optimization, you balance speed and efficiency, ensuring you get the best filtration performance for your specific needs.
How Do Temperature Changes Influence Pore Size Effectiveness?
Temperature changes can impact pore size effectiveness through thermal expansion, which causes the membrane to expand or contract. If you’re working in environments lacking temperature stability, pore sizes might shift, reducing filtration efficiency or allowing unwanted particles through. To guarantee consistent results, maintain stable temperatures and choose membranes designed to resist thermal expansion. This way, you keep pore sizes effective and filtration reliable regardless of temperature fluctuations.
Are There Compatibility Issues With Certain Chemicals?
Imagine your filtration process as a delicate dance, where chemical compatibility is the rhythm and pH stability the steady beat. Certain chemicals can react with membrane materials, causing degradation or clogging. You need to verify the chemical compatibility and pH stability of your membrane before use. This ensures your filtration remains smooth, preventing damage and ensuring reliable results without any compatibility issues disrupting your workflow.
Can Pore Size Be Customized for Specific Applications?
Yes, you can customize pore size for specific applications by using application-specific membranes. Pore size customization allows you to select membranes tailored to your filtration needs, whether you’re filtering out fine particles or larger contaminants. This guarantees ideal efficiency and precision in your processes. Consult with manufacturers to find or create membranes with the exact pore size required for your unique application, improving results and reducing waste.
What Maintenance Practices Ensure Membrane Longevity?
You keep your membrane in top shape by following proper cleaning protocols and storing it correctly—don’t let it go to seed. Regular cleaning prevents buildup and clogs, extending its life, while storing it in appropriate conditions avoids damage. Handle with care, avoid harsh chemicals, and keep it dry and cool. This way, you guarantee your membrane stays effective and lasts longer, saving you time and money in the long run.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve learned how to choose the perfect membrane pore size, you’re practically a filtration superhero! With the right pore size, you can filter faster than a lightning bolt and achieve crystal-clear results effortlessly. Remember, selecting the right membrane isn’t just important—it’s the secret weapon in your laboratory arsenal. So go ahead, master vacuum filtration, and make your experiments as smooth as silk. Your future self will thank you for this game-changing knowledge!